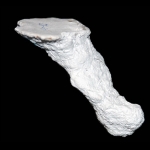
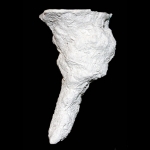
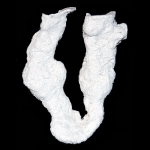
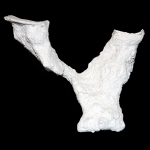
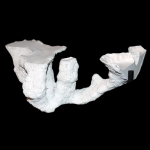
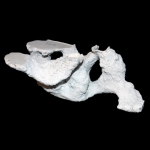
Mastigoproctus giganteus produces six different burrow architectures each with multiple variations.
Open burrows are used as temporary shelters to permanent dwellings. Components of the burrows include one to six surface openings, shafts, tunnels, and laterally expanded chambers. Burrow elements vary in orientation from nearly horizontal (5-10 degrees), oblique (30-45 degrees), and vertical (75-90 degrees). Mazeworks may contain shafts, tunnels, and chambers with all of these orientations. Shafts, tunnels, and chambers are elliptical in cross section (W/H ratio ~1.9). The floor, roof, and walls are curves outward, although floors and roofs may be flattened. Shaft and tunnel widths are irregular along their length and typically straight except in J- and U-shaped burrows. Branching occurs in Y-shaped burrows and mazeworks. Chambers are typically located at the end of the burrow except in mazeworks where multiple chambers may be present along the length of different tunnels. The tops and sides of the tunnels tend to be irregular with several protrusions and divots, whereas the bottoms are smooth and even. Small sets of paired protrusions occur on the walls; these are produced by the pedipalps during excavation.
Additional resources are available within the downloadable PDF files linked at the bottom of the page
Additional resources
Giant Vinegaroon Burrow Catalog (PDF)
Giant Vinegaroon Burrow Information Packet (PDF)
Giant Vinegaroon Burrow Data Spreadsheet (Microsoft Excel – Auto Download)